Malaysia is gearing up for the E-Invoicing revolution in 2024, and it’s crucial for businesses to understand the ins and outs of this new system. In this guide, we will walk you through everything you need to know about Malaysia’s E-Invoicing initiative.
We’ll cover the requirements set by the Inland Revenue Board (IRB), integration with accounting systems, and the key characteristics of Malaysia’s electronic invoices.
NOTE: We trained an AI Assistant on IRB Malaysia e-Invoice Guideline Version 4.0, IRB Malaysia e-Invoice Specific Guideline Version 3.1 and IRB Malaysia e-Invoice General FAQs as a reference. You can try out this AI bot by visiting our LHDN e-Invoicing AI Assistant post.
First off, here are some FAQs for your convenience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is e-invoicing mandatory in Malaysia?
Indeed, starting from 2024, e-invoicing will be a requirement for businesses in Malaysia. The government is gradually introducing this system, following the phased introduction of mandatory electronic invoicing in Malaysia starting from 1st August, 2024, to streamline business operations and improve efficiency.
Businesses, including all individuals and legal entities must adopt e-invoicing to comply with these new rules, which bring benefits such as less paperwork, quicker payment processes, increased accuracy in invoicing, and the gradual introduction of electronic invoicing in the country. The Malaysian Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) has confirmed in a briefing that they will be involved in the implementation of e-invoicing in Malaysia.
From 1 August 2024 onwards, the mandate for e-invoicing will be phased in based on annual turnover or revenue thresholds.
Here’s the updated e-invoice implementation timeline:
The Malaysian government has announced an updated timeline for the mandatory adoption of e-invoicing, as part of the recent 2024 budget proposals. The previous multi-year phased rollout has been consolidated into a faster transition:
| Targeted Taxpayers | Implementation Date |
| Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM100 million | 1 August 2024 |
| Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM25 million and up to RM100 million | 1 January 2025 |
| All taxpayers | 1 July 2025 |
While e-invoicing is obligatory for businesses meeting the specified turnover thresholds, taxpayers are welcome to voluntarily implement e-invoicing before their mandated phase.
UPDATED 02 Jul 2024: Micro SMEs earning below RM150,000 annually exempted from e-invoicing, says Amir Hamzah | The Star (However, do note that MSMEs below RM150k are still needed to submit monthly consolidated e-invoices).
We recommend start investing in Cloud Accounting software to be ready for this. Do check out our Top e-Invoice Accounting Software Options in Malaysia 2024 article for some options.
Interim Relaxation Period
- Purpose: The interim relaxation period is designed to ensure a smooth transition and implementation of the e-Invoice system.
- Duration: The relaxation period is six months from the mandatory implementation date for each phase.
- Targeted Taxpayers:
- Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM100 million: 1 August 2024 to 31 January 2025.
- Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM25 million and up to RM100 million: 1 January 2025 to 30 June 2025.
- All other taxpayers: 1 July 2025 to 31 December 2025.
- Options During the Period:
- Taxpayers can issue consolidated e-Invoices for all activities and transactions.
- Consolidated self-billed e-Invoices can be issued for self-billed circumstances.
- Flexibility in inputting information in the “Description of Product or Service” field.
- System Readiness:
- Taxpayers whose systems are ready can opt to issue individual e-Invoices and self-billed e-Invoices instead of using the relaxation provisions.
- Monthly Issuance:
- Taxpayers are required to issue consolidated e-Invoices and self-billed e-Invoices on a monthly basis.
What are the regulations for e-invoicing?
The regulations for e-invoicing can differ across countries and jurisdictions. They typically involve using electronic formats and standardized protocols. Essential details such as the buyer and seller information, invoice number, date, and taxable amount, including foreign invoices, must be included.
It’s also important to include the tax identification number (TIN) of buyers, which may not be readily available in some systems. It is crucial to adhere to these rules to avoid penalties and ensure smooth business operations.
In Malaysia, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) has issued the E-Invoice Guideline that outlines the rules for e-invoicing. This guide provides comprehensive instructions and requirements for implementing e-invoicing.
Here are some key regulations for e-invoicing in Malaysia:
- Standardized Format: E-invoices must use a standardized format specified by the IRBM, which is generally based on XML or JSON standards for consistency and compatibility.
- Mandatory Data Fields: E-invoices must include specific mandatory data fields like invoice number, date, seller and buyer information, line items, quantities, prices, taxes, and totals. Adherence to these mandatory fields is crucial for regulatory compliance.
- Digital Signatures: E-invoices often require digital signatures for authenticity and integrity. These signatures confirm that the e-invoice data comes from a specific taxpayer and hasn’t been altered.
- Validation and Clearance: E-invoices must pass validation checks for format, structure, and data field accuracy. Once validated, the e-invoice receives clearance, indicating it meets regulatory standards.
- Integration with Tax Authority: E-invoices may need to integrate with the tax authority’s systems or platforms. This integration allows seamless transmission of e-invoices to the tax authority for processing and auditing purposes.
- Record-Keeping: Businesses are required to keep records of e-invoices as per the record-keeping requirements specified by the IRBM. These records should be securely stored and readily accessible for audit purposes.
- Phased Implementation: The mandatory implementation of e-invoicing in Malaysia is being carried out in phases based on annual turnover or revenue thresholds. Different phases have different deadlines for mandatory compliance.
What is the difference between an e-invoice and a digital invoice?
An e-invoice refers to an invoice that is both generated and transmitted electronically, often conforming to a standardized format. A digital invoice, however, includes any invoice created and stored digitally, irrespective of its transmission method. E-invoices are typically more structured and can be easily integrated with accounting systems, thereby offering automated payment processing and real-time tracking.
More specifically:
E-Invoice:
An e-invoice, or electronic invoice, is an invoice that is created, sent, and received in an electronic format instead of traditional paper-based formats. It is a digital representation of a transaction between a supplier and a buyer. E-invoices generally follow a standardized format and contain structured data fields that capture essential information. E-invoices can be created, exchanged, and processed electronically, thereby eliminating the need for manual handling and paperwork.
In certain B2C transactions where the end consumer does not need e-Invoices to support the transactions for tax purposes, suppliers are allowed to issue normal receipts/invoices based on current practices.
Digital Invoice:
A digital invoice is a broader term that includes any invoice that exists in a digital or electronic form. This includes not only e-invoices but also invoices in other digital formats such as PDF, Word documents, or even scanned images of paper invoices. Digital invoices may not necessarily adhere to a standardized format or have structured data fields like e-invoices. They can be created using various digital tools or software, but they may still require manual handling or conversion into a standardized format for processing or integration with other systems.
In short, while e-invoices refer specifically to standardized electronic invoices with structured data fields, digital invoices encompass a wider range of invoices in digital formats, including both structured and unstructured formats.
What is the National e-Invoicing Initiative in Malaysia?
The National e-Invoicing Initiative in Malaysia is a government-led effort designed to promote the adoption of e-invoicing among businesses in the country. The initiative is driven by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) and is part of the government’s broader digital transformation strategy.
The key objectives of this e-invoicing initiative include:
- Enhancing Efficiency: The initiative aims to streamline and digitize the invoicing process, reducing manual efforts, paperwork, and errors associated with traditional paper-based invoicing.
- Improving Tax Compliance: E-invoicing enables real-time or near-real-time validation of invoices, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and reducing the risk of fraud or non-compliance.
- Promoting Digital Economy: The initiative supports the growth of the digital economy by encouraging businesses to embrace digital technologies and processes, fostering innovation and competitiveness.
- Facilitating Business-to-Government (B2G) Transactions: E-invoicing facilitates seamless and efficient invoicing between businesses and government entities, improving transparency, reducing administrative burdens, and enhancing collaboration.
- Supporting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): The initiative provides support and resources to help SMEs adopt e-invoicing, enabling them to benefit from the efficiency gains and cost savings associated with digital invoicing.
The National e-Invoicing Initiative in Malaysia involves the development of guidelines, standards, and technical infrastructure to facilitate the implementation of e-invoicing. It includes the establishment of a centralized e-invoicing platform, known as MyInvois Portal, which allows businesses to create, submit, validate, and store e-invoices.
The initiative also involves engagement sessions, training materials, and assistance provided by the IRBM to support stakeholders in understanding and implementing e-invoicing.
What are the benefits of e-invoicing Malaysia?
Increased Efficiency: E-invoicing automates the invoicing process, reducing manual tasks and paperwork. This can significantly increase efficiency and productivity in businesses.
Cost Savings: By reducing the need for paper invoices and manual processes, e-invoicing can result in significant cost savings. This includes savings on printing, mailing, and storage costs, as well as savings from reduced manpower requirements.
Improved Accuracy: E-invoicing minimizes the risk of human error that can occur during manual data entry. It also ensures accuracy in calculations, preventing mistakes that could lead to disputes or delays in payment.
Faster Payment Cycles: E-invoices can be delivered instantly and processed more quickly than paper invoices. This can lead to faster payment cycles, improving cash flow for businesses.
Integration with Digital Systems: E-invoices can easily be integrated with other digital systems and platforms such as accounting software, ERP systems, and tax reporting tools. This makes it easier to manage financial data and improves overall business operations.
Improved Traceability and Transparency: E-invoicing provides a clear audit trail, making it easier to track invoices and payments. This improves transparency and can help to prevent fraud and non-compliance.
Enhanced Supplier-Customer Relationships: E-invoicing can improve communication and relationships between suppliers and customers. E-invoices can be easily accessed and reviewed, leading to fewer disputes and better customer satisfaction.
Regulatory Compliance: E-invoicing helps businesses comply with tax regulations in Malaysia. With the government’s mandate for e-invoicing, businesses that adopt e-invoicing will be better prepared to meet these requirements.
Real-Time Tracking and Reporting: E-invoicing allows for real-time tracking and reporting of invoices and payments. This can provide valuable insights for businesses, helping them to make informed decisions.
Data Analytics and Insights: The structured data from e-invoices can be used for data analytics, providing businesses with valuable insights into their sales, expenses, and overall financial performance. This can help businesses to identify trends, make predictions, and optimize their strategies and operations.
For more FAQs, I would recommend checking out the IRB very complete Frequently Asked Questions page.
Now, let’s move on to the comprehensive guide.
Understanding Malaysia E-Invoicing Regulations for 2024
Malaysia’s e-invoicing system aims to streamline and digitize the invoicing process for businesses in the country, ultimately improving the efficiency of Malaysia’s tax system and having a positive impact on the economy. By adopting electronic invoicing, businesses can enjoy benefits such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved accuracy, and faster payment cycles.
The key features and requirements of the e-invoicing system include the use of QR codes, compliance with specific formats like XML or PDF, integration with the MyTax portal, and seamless integration with the integrated tax return filing system.
This initiative, known as the National E-Invoicing Initiative, aims to increase business efficiency by eliminating manual data entry and physical paper handling processes. Especially when it is going to be joining the PEPPOL network later on, and that’s 1 big step to join the global digitalization movement.
To implement e-invoicing in Malaysia, businesses need to register with the government, adhere to the regulations set by the tax authorities, and ensure their invoices are verified by the Malaysian Inland Revenue Board (IRB). While there are challenges and key considerations in adopting e-invoicing, including changes in accounts payable functions, following best practices can lead to successful pilot implementation and compliance with the regulations.
The Malaysian Inland Revenue Board (IRB) provides further guidance on the mandatory e-invoice implementation, which includes updated guidelines on the gradual roll-out for targeted taxpayers.
Malaysia’s e-invoicing regulations for 2024 aim to enhance the efficiency of tax administration and promote the digital economy. The implementation of e-invoicing will be mandatory for taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue exceeding RM100 million, starting from 1 August 2024.
Do take a look at this updated e-invoicing implementation timeline from IRB below

Updated with Phase 4 & Exemption: e-Invoicing delayed to 2026 for SMEs (RM 150k – RM 500k)
Decoding the IRB Requirements for E-Invoicing
Understanding the requirements set by the Inland Revenue Board (IRB) of Malaysia is crucial when implementing an e-invoicing system. Compliance with IRB regulations ensures smooth integration of electronic invoices into your business processes.
However, transitioning to e-invoicing also comes with challenges and considerations. To ensure a successful transition, businesses should follow a step-by-step approach that includes verifying the IRB guidelines and integrating them into their systems. By doing so, they can enjoy the benefits of e-invoicing while adhering to the necessary regulations.
Our recommendation for businesses is to check with their existing tax agent, or accounting firm for guidance on operations related matter. Meanwhile, also check with their software vendor on what’s the plan for software updates to be compliance with the IRB requirements.
The Role of Information Technology in the E-Invoicing System
Information technology plays a pivotal role in facilitating the implementation of Malaysia’s e-invoicing system. With robust IT infrastructure, businesses and government agencies can securely transmit electronic invoices. IT ensures accurate data capture, validation, and storage, minimizing errors and seamlessly integrating with existing systems.
E-invoicing software and platforms leverage IT capabilities to automate invoice generation, processing, and archiving. Real-time tracking and monitoring of invoices are made possible through IT solutions, enhancing transparency and ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Most of the local prominent accounting software will most likely be updated to include this e-invoicing system. Therefore, businesses that currently uses local accounting system are less likely to face any issue, and the software vendor will provide support and guidance for this e-invoicing implementation.
The Role of QR Code in E-Invoices
QR codes play a crucial role in e-invoicing by enabling quick and accurate scanning for seamless data retrieval. They contribute to reducing errors and improving the efficiency of invoice processing. With the inclusion of QR codes, easy verification and authentication of e-invoices are ensured. These codes also enhance security by providing a unique identifier for each e-invoice.
Additionally, businesses can easily track and trace invoices using QR codes, which is essential for audit and compliance purposes. By incorporating QR codes into e-invoices, companies can streamline their operations and ensure the validity, accuracy and security of their invoicing processes.
It is very important to scan the QR code on those e-invoices to check on its validation, especially if those e-invoices will be used later in any tax deductions.
Key Characteristics of Malaysia’s Electronic Invoices
Malaysia’s electronic invoicing system offers several key characteristics that businesses should be aware of.
Firstly, e-invoicing brings numerous benefits to businesses in Malaysia, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and faster payment processing. Secondly, there are specific legal frameworks and regulations governing e-invoicing in Malaysia, ensuring compliance with tax authorities such as the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRB).
Additionally, Malaysia’s e-invoicing system requires certain key features and requirements to be met, such as the use of XML or PDF formats and the inclusion of a certified serial number. Implementing an e-invoicing system involves steps like integrating with the LHDNM’s e-invoicing API (Application Programming Interface) and adapting to the new regulations set by the Ministry of Finance to meet specific needs of businesses.
Do take a look at this e-invoice overview workflow and invoicing process overview from IRB below.
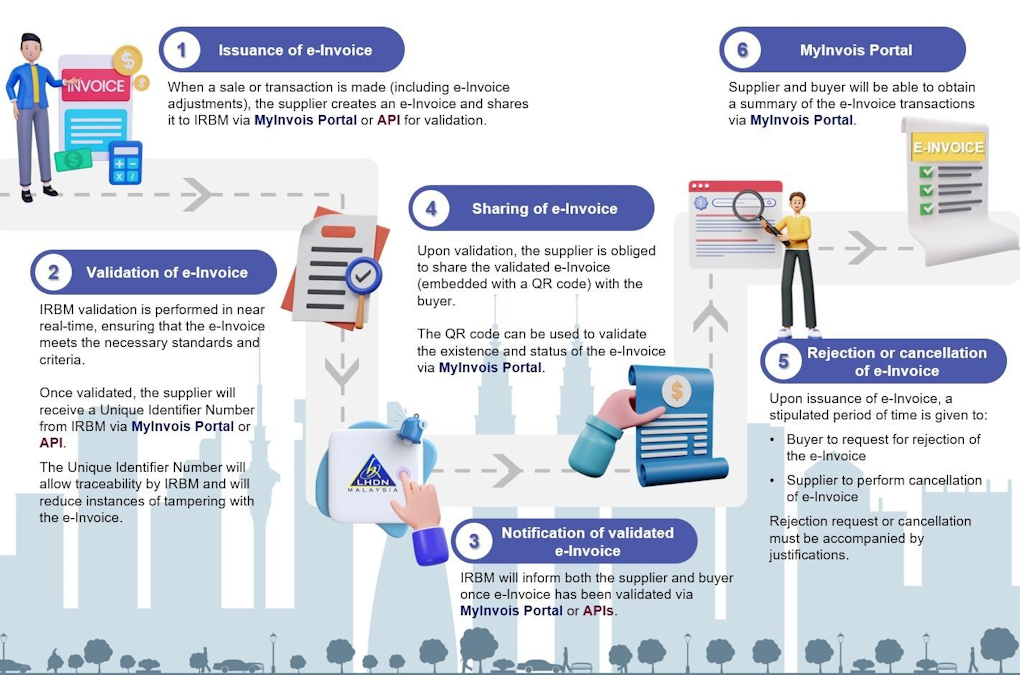

Understanding E-Invoice Models
Malaysia’s e-Invoicing system comprises two primary models: the MyInvois Portal and API Integration. The former MyInvois Portal is aimed at micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), while the latter e-invoicing API is designed to cater to larger taxpayers who handle a high volume of transactions.
Here, we’ll break down both models and guide you through their procedures.
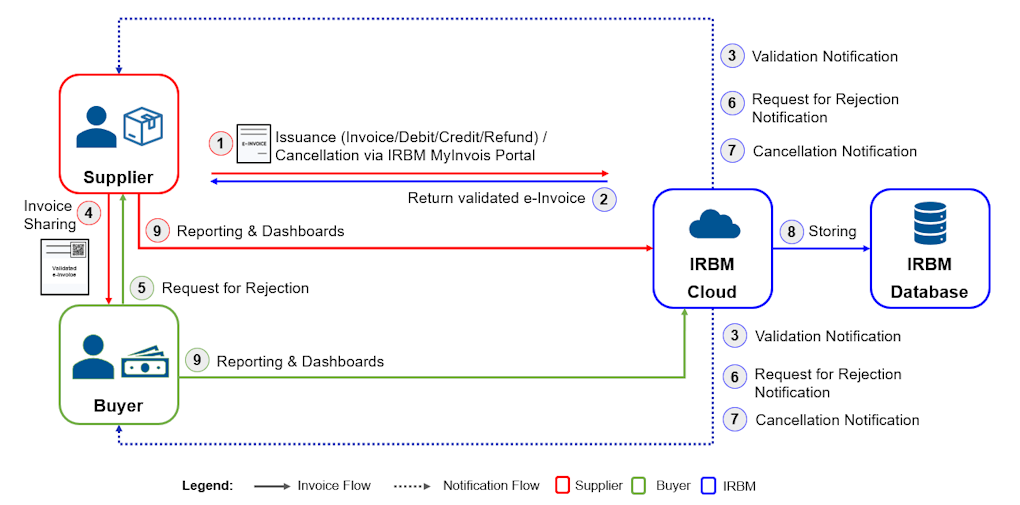
Workflow of E-Invoicing
Let’s take a broad look at the e-Invoice workflow. This process starts when a sale is made or a transaction is undertaken on a monthly basis. An e-Invoice is then issued by the supplier via the MyInvois Portal or API. The workflow concludes with the storage of cleared e-Invoices on IRBM’s database, enabling taxpayers to view their historical e-Invoices.
Do take a look at this e-invoicing process from IRB below.

E-Invoicing via MyInvois Portal
The MyInvois Portal is the best way for SMEs that unable to issue e-Invoices from their own systems. Here’s how it works:
- Log in to MyInvois Portal using your MyTax credentials.
- Create e-Invoices individually by filling out a form or you can upload the files in proper format to generate them in batches.
- Submit those created e-Invoices to IRBM via the portal for validation.
- Receive validated e-Invoices returned with an IRBM unique identifier to be traceable.
- Notifications are sent to the supplier and buyer upon e-Invoice validation.
- Share the cleared e-Invoice containing IRBM’s QR code with the buyer.
- Within 72 hours of validation, the buyer still can request rejection or the supplier can cancel the e-Invoice.
- Accepted e-Invoices are stored in IRBM’s database.
- Retrieve e-Invoice data from the portal in various formats.
This user-friendly portal enables taxpayers, particularly smaller ones, to meet e-Invoicing obligations with minimal investment in additional technology or systems.
E-Invoicing via API Integration

For those dealing with higher volumes of invoices, API Integration with IRB’s MyInvois system is the way forward.
To get started with the API model, you or your tech provider will need to:
- Set up callback addresses (system endpoints for receiving the IRB’s API responses).
- Log into IRB’s APIs using digital certificates issued by IRB.
- Configure your API integration per the Software Development Kit (SDK), expected to be issued in Q4 of 2023.
Here’s the process once you’re set up:
- Create and submit e-Invoices via API in the standard format.
- Await validation by IRB via APIs – if any errors occur, usually they’ll be returned the error code / description.
- Notifications are sent to the Supplier and Buyer upon e-Invoice clearance.
- Share the cleared e-Invoice with the Buyer.
- The Buyer or Supplier can reject or cancel the e-Invoice within 72 hours of validation.
- Accepted e-Invoices are stored in IRB’s database.
- Retrieve e-Invoice data via APIs.
Although API integration requires some upfront investment in technology, it provides seamless transmission of high volumes of e-Invoices, making it a worthwhile consideration for larger businesses.
Key Impacts of E-Invoicing on Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Malaysia
We’ll be exploring the significant impacts and considerations that e-Invoicing brings to Malaysian Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs):
Gradual Implementation:- The phased implementation based on turnover thresholds offers SMEs more time to transition than their larger counterparts. This approach provides breathing space and ensures a smooth transition into e-Invoicing.
Accessible Platforms:- Platforms like MyInvois offer an accessible channel for SMEs to issue e-Invoices without needing massive investments in technology integration, making it efficient and cost-effective.
Necessary Adjustments:- Transitioning to automated e-Invoicing may require SMEs to tweak their processes, bookkeeping, and staff capabilities. These adjustments might include changes in recording transactions, issuing invoices, and managing credits/debit notes.
Preparing Data Requirements:- Data such as Tax ID numbers and appropriate product codes need to be prepared ahead of the transition to ensure compliance and accuracy in e-Invoicing.
Advanced Features:- Advanced features, including batch upload, may require staff training and modifications to internal systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
Assistance from Vendors:- Vendors offering accounting software and services can assist in the transition by building e-Invoicing compatibility into existing systems, ensuring seamless integration.
Utilizing API Integration:- Larger SMEs may consider leveraging API integration for enhanced efficiency, while smaller SMEs can maximize the use of platforms like MyInvois portal.
Error Reduction:- Even without full automation, utilizing platforms like the MyInvois portal can minimize manual errors and paperwork compared to traditional invoicing, providing a more streamlined process.
Enhanced Financial Reporting:- The proper adoption of e-Invoicing can improve financial reporting, cash flow visibility, and tax filing for SMEs through centralized data, leading to better business insights.
In essence, while some process changes may be necessary, the impact on SMEs is manageable due to the extended transition timeframe and accessible options like the MyInvois portal.
The benefits of migrating to e-Invoicing in Malaysia undoubtedly outweigh the effort required.
How Can Businesses Prepare for the New E-Invoice Regulations?
Preparing your business for the new e-invoice regulations in Malaysia involves familiarizing yourself with the requirements, updating your accounting software, training your staff, and communicating with suppliers and customers for a smooth transition.
To prepare for the new e-invoice regulations, businesses can take the following steps:
1. Understand the Regulations:
Familiarize yourself with the specific e-invoice regulations applicable in Malaysia. Study the guidelines, requirements, and timelines provided by the tax authorities. Ensure you have a clear understanding of the obligations and compliance standards.
2. Assess Internal Systems and Processes:
Evaluate your existing invoicing systems and processes to identify any gaps or areas that need adjustment to comply with the e-invoice regulations. Determine if your current systems can generate e-invoices in the required format and capture the necessary data fields. Consider any necessary upgrades or modifications.
3. Select E-Invoicing Software or Service Provider:
Choose an e-invoicing software or service provider that aligns with the regulatory requirements and meets your business needs. Look for solutions that offer features such as generating compliant e-invoices, data validation, digital signatures, integration capabilities, and secure storage options.
Can refer to our Top e-Invoice Accounting Software Options in Malaysia 2024 article for more e-invoicing software.
4. Implement System Integration:
Integrate your chosen e-invoicing solution with your existing accounting or ERP systems. Ensure seamless data flow between different systems to automate the creation, validation, and transmission of e-invoices. This integration will streamline your invoicing processes and reduce manual efforts.
To understand more about 3 main types of e-invoicing solutions available in Malaysia, can refer to our E-Invoicing Solutions in Malaysia: e-Invoice Malaysia for SMEs article.
5. Train Employees:
Provide training and education to your employees on the new e-invoice regulations and the updated processes. Ensure they understand the importance of compliance, how to generate and handle e-invoices, and any changes in their roles or responsibilities related to invoicing.
6. Update Contracts and Agreements:
Review and update your contracts, agreements, and terms and conditions to include provisions related to e-invoicing. Ensure that your agreements reflect the new requirements and specify the format, delivery methods, and any additional information needed for e-invoices.
7. Test and Validate:
Conduct thorough testing of your e-invoicing system to ensure it generates compliant e-invoices and meets the validation criteria set by the tax authorities. Validate the accuracy of the data fields, tax calculations, digital signatures, and any other requirements specified in the regulations.
8. Establish Record-Keeping Procedures:
Develop robust record-keeping procedures to store and retain e-invoices as per the regulatory requirements. Ensure you have secure and accessible storage systems in place to maintain the integrity and availability of your e-invoice records.
9. Stay Updated and Seek Professional Advice:
Regularly monitor updates and changes in the e-invoice regulations. Stay informed about any new guidelines or amendments issued by the tax authorities. Consider seeking professional advice from tax consultants or experts to ensure ongoing compliance with the evolving regulations.
Do check out our e-Invoices services offering if you need any help implementing e-invoicing.
What Comes Next After the Implementation of E-Invoicing?
After the implementation of e-invoicing, businesses should focus on ensuring compliance with the system. They should regularly monitor and review the processes to identify any areas for improvement. Staying updated with any changes in regulations is crucial for maintaining compliance.
After the implementation of e-invoicing, businesses can expect several potential developments and benefits.
Here are some key aspects that may follow the implementation of e-invoicing:
1. Streamlined Processes:
E-invoicing streamlines the entire invoicing process, from creation to delivery and payment. It eliminates manual tasks, reduces paperwork, and minimizes errors, leading to more efficient and streamlined processes within the organization.
2. Faster Payments:
E-invoicing facilitates faster payment cycles as invoices can be delivered instantly and accurately to the recipients. This can help improve cash flow management for businesses, reducing the time between invoicing and receiving payments.
3. Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance:
E-invoicing reduces the risk of errors and discrepancies in invoices. The standardized format and automated validation processes ensure accurate data entry and compliance with regulatory requirements, minimizing the chances of audits or penalties.
4. Improved Supplier-Customer Relationships:
E-invoicing promotes better collaboration and communication between suppliers and customers. The seamless exchange of electronic invoices enhances transparency, reduces disputes, and strengthens relationships based on trust and efficiency.
5. Real-Time Tracking and Reporting:
E-invoicing enables real-time tracking of invoice status, from creation to payment. Businesses can monitor the progress of invoices, identify bottlenecks, and generate reports for better financial analysis and decision-making.
6. Cost Savings:
E-invoicing reduces costs associated with paper-based invoicing, printing, postage, and manual processing. It eliminates the need for physical storage and retrieval of paper invoices, resulting in significant cost savings over time.
7. Integration with Business Systems:
E-invoicing can be integrated with other business systems such as accounting software, ERP systems, and payment gateways. This integration enables seamless data flow, automates reconciliation processes, and improves overall operational efficiency.
8. Data Analytics and Insights:
With e-invoicing, businesses have access to a wealth of digital invoice data. This data can be leveraged for analytics, providing insights into customer behavior, payment patterns, and financial trends. These insights can inform strategic decision-making and help optimize business operations.
9. Potential for Supply Chain Financing:
E-invoicing data can be utilized for supply chain financing programs. The availability of accurate and verifiable invoice data can help businesses secure financing based on their outstanding invoices, improving cash flow and working capital management.
10. Future Digital Transformation Opportunities:
E-invoicing serves as a foundation for further digital transformation initiatives within the organization. It opens doors to explore other digital solutions such as electronic payments, automated procurement processes, and advanced data analytics.
Conclusion
The implementation of the E-Invoicing system in Malaysia marks a significant shift towards digitalization and efficiency in business processes. With the deadline approaching in 2024, it’s crucial for businesses to understand and prepare for this revolution. By integrating your accounting system with E-Invoicing and adhering to the requirements set by the IRB, you can ensure smooth compliance.
Additionally, creating and converting invoices to XML format and understanding the process of LHDNM’s E-Invoicing API are essential steps to sending compliant E-Invoices. The use of QR codes in E-Invoices adds an extra layer of convenience and security.
To stay ahead of the curve, businesses must start preparing now and embrace the opportunities that the E-Invoicing system brings. Remember to try out our LHDN e-Invoicing AI Assistant and share this guide to help others navigate this transition smoothly.
Need help with LHDN e-Invoice compliance? Check out our e-Invoice services – we’ve got you covered!
UPDATE: LHDN e-Invoicing SDK with API beta version launched on 9th February 2024.
Software Development Kit (SDK) for Inland Revenue Board Of Malaysia (IRBM) MyInvois System have been launched at Software Development Kit (SDK) for Inland Revenue Board Of Malaysia (IRBM) MyInvois System (hasil.gov.my).
MyInvois is the solution of the Inland Revenue Board Of Malaysia (IRBM) used by taxpayers to submit their issued documents with the Tax Authority. Generally referring to the compliance of e-invoicing. The IRBM MyInvois site contains documentation of the APIs exposed to taxpayer ERP / Accounting systems that can be used to integrate with MyInvois System to automate the document processing.
Local Malaysia accounting software developer will most likely be utilizing this SDK to update their respective accounting software to be integrated with the MyInvois API.






